Comparison of OLED / STN LCD / VFD
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) has a far higher resolution with a faster response time, a wider viewing angle, superior brightness, thin, light weight and contrast in comparison with LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) and VFD (Vacuum Fluorescent Display).
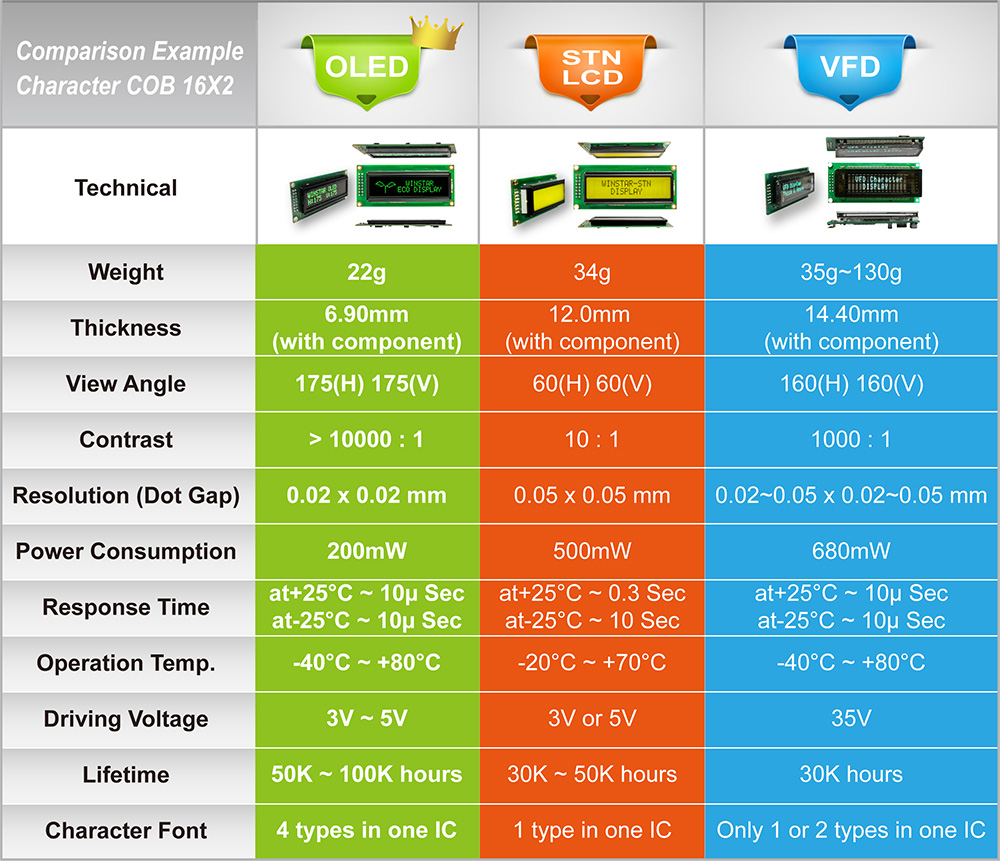
The following table is the comparison of OLED/STN LCD/VFD displays. We used a character 16x2 COB structure module as an example. Welcome to explore the advantages of OLED displays, and you would find OLED display is not a choice but a necessity to your applications.
 175 degree
175 degree
OLED's emitting area is the entire front surface, it has the widest viewing angle because it does not need a backlight attachment like STN LCD displays. As to the VFD Display, the display surface is placed in a deeper position, the sealing frames and the grid frames make the viewing angles smaller.
| Display Type | OLED | STN LCD | VFD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Viewing Angle | >175(H) 175(V) | 60(H) 60(V) | 160(H) 160(V) |
10 μsec – Response time
OLEDs also have a faster response time than LCDs. Whereas the normal LCDs currently have a 200 ms response time due to the nature of liquid crystal, as to OLEDs, its response time can less 10μ sec at 25 ℃.
| Display Type | OLED | STN LCD | VFD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Response Time | at +25℃ - 10µ Sec | at +25℃ - 0.2 Sec | at +25℃ - 10µ Sec |
| at -20℃ - 10µ Sec | at -20℃ - 4 Sec | at -20℃ - 10µ Sec |
-40℃ ~ 80℃
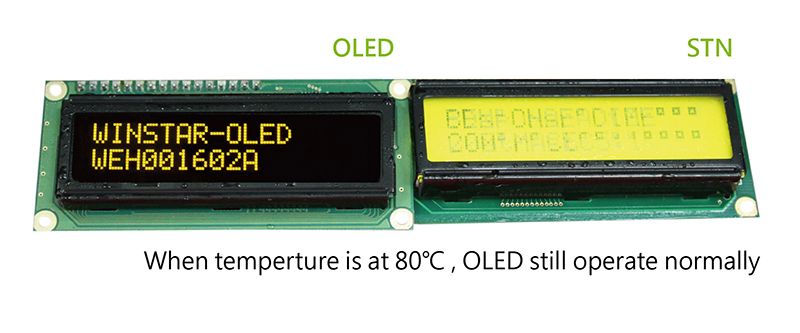
Comparing with conventional STN LCD displays, OLEDs featured with wider operation temperature range -40 ℃ ~ 80 ℃. The nature of OLED technology is self-luminous; the OLED displays still can work at rugged environment. It is very obvious especially at lower operation temperature; the OLED display works excellent. Some STN LCD modules could be workable at lower temperature or with heater on LCD module, but the response time at lower temperature will be longer than normal temperature since the liquid crystal has been frozen.
No need backlight
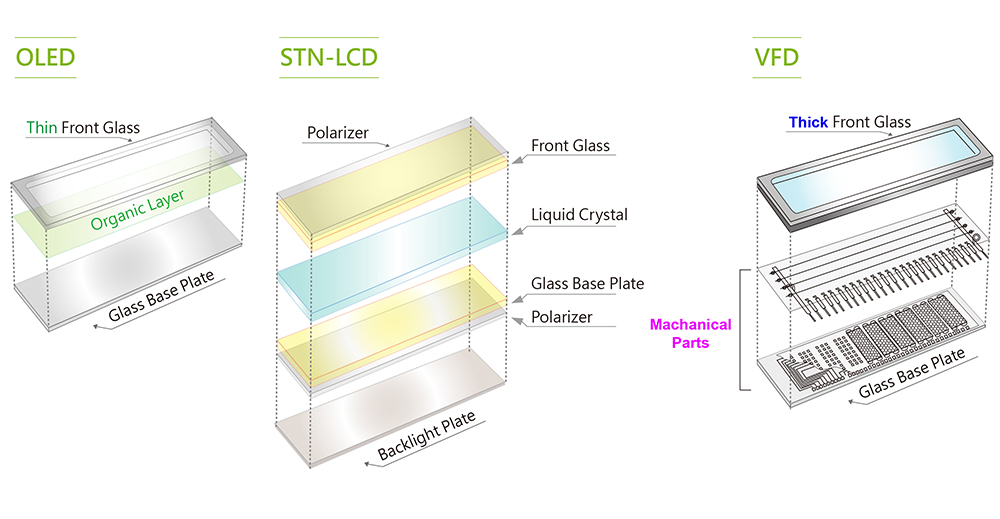
A significant advantage of OLED displays over traditional liquid crystal displays (LCDs) is that OLEDs do not require a backlight to function, OLED is self emitting. OLED layers are applied directly to the surface of the glass substrate and this allows the display area to be extended to the edge of the glass substrate, which requires no backlight and make the displays very thin.
VFD display is self-luminous as well, but VFD needs the mechanical parts mounted around the display frame. VFD needs thick, strong sealing glasses for vacuum encapsulation which makes the VFD very thick.
Below is an example of COB structure 16x2 character modules of OLED, STN-LCD and VFD comparison on thickness.
| Display Type | OLED | STN LCD | VFD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Module Thickness | 6.90 mm | 9.70 mm | 14.40 mm |
| (e.g.: COB 16x2) | (with component) | (with component) | (with component) |


200mW Low Power Consumption
OLED uses only the power needed to display what is displayed. The power consumption changes depending on each lighting ratio. The STN-LCD display usually requests a backlight such as LED which requests power to turn on LEDs. The VFD needs two power supplies for the pixel display and the filament. The filament power makes up a large percentage and is constant, regardless of the pixels displayed.
| Display Type | OLED | STN LCD | VFD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Driving Voltage | ~3 - 5 V | ~ 3 - 5 V | ~35 V |
| Power use at 100% lighting (e.g.:COB16x2) | ~200 mW | ~500 mW | ~680 mW |
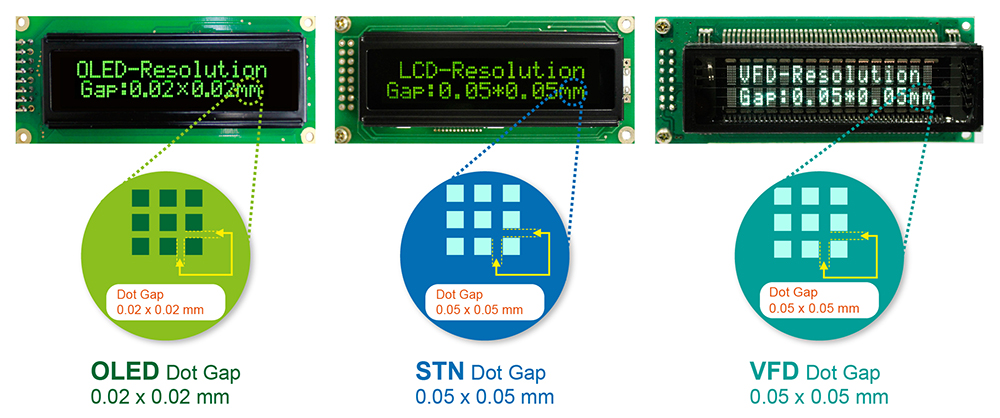
0.02 x 0.02 mm
OLED layers are applied directly to the surface of the glass substrate and OLED using a high precision mask which allows OLED to produce high resolution display; its dot gap can lower to 0.02x0.02mm. As to VFD, it requires mechanical parts to produce emitting device. The mechanical parts for VFD require is very strict. The precision of VFD emitting mechanical parts is limited and that requires dot gap is 0.05x0.05mm.
| Display Type | Winstar OLED | STN LCD | VFD in market |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution | Gap:0.02x0.02mm | Gap:0.05x0.05mm | Gap:0.02~0.05x 0.02~0.05mm |