An introduction to wide viewing angle display for VATN-LCD
An introduction to wide viewing angle display for VATN-LCD
Three LCD technologies dominate the market:
- TN (twisted nematic mode)
- VA (vertical alignment mode)
- ÍPS (in-plane switching mode)
The VA display technologies can be categorized into three groups:
- MVA (multi-domain vertical alignment) from Fujitsu
- PVA (patterned vertical alignment) from Samsung
- CPA (continuous pinwheel alignment) from Sharp
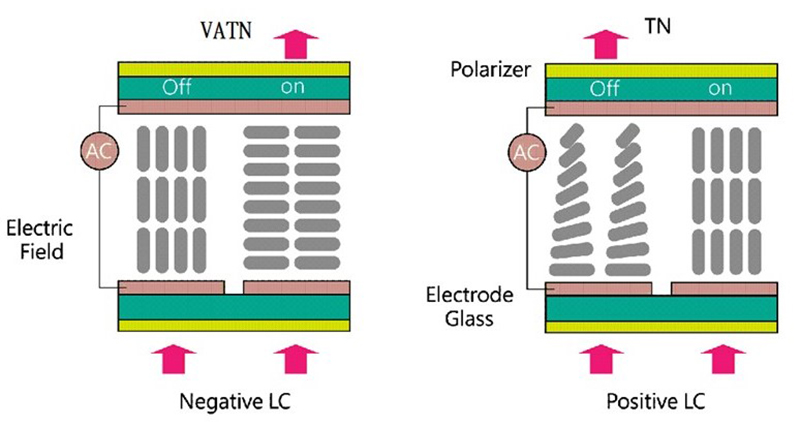
Before power-on, the alignment of the liquid crystals is perpendicular to the glass, unlike the TN LCD, which is parallel with the glass substrate. As figure1 shows, the light would be blocked by the polarizer while traveling through and therefore appears black.
After being hit by voltage, the liquid crystals will be tilted and moved. With the tilted liquid crystals, it will be easier for the light to travel through the polarizer, and therefore the display appears whitish. In terms of visual contrast, VATN will perform better than TN.
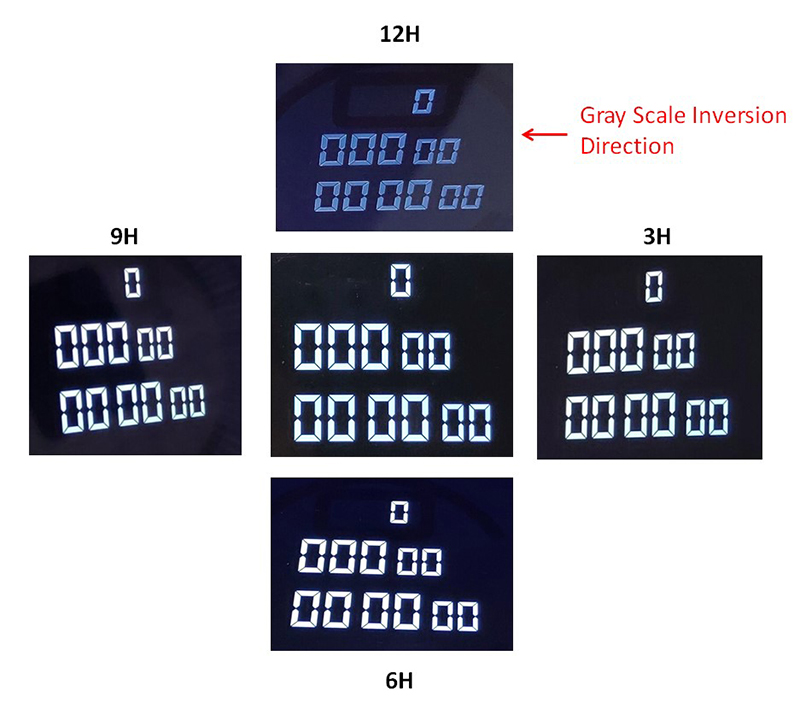
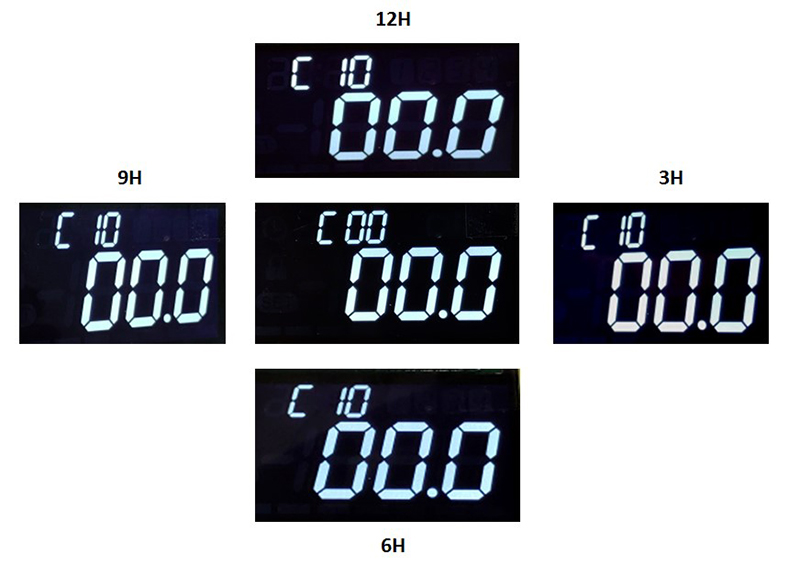
With the formation of the VATN liquid crystals, the “blind spot” (or Gray-Scale Inversion) would appear within certain viewing angles, as photo No.2 shows.
Because of the rotation angles of liquid crystals, the light traveling through would become directional, causing light and color deviation. It is the primary cause of the so-called Gray-Scale Inversion and color deviation.
■ Cause for Gray-Scale Inversion:
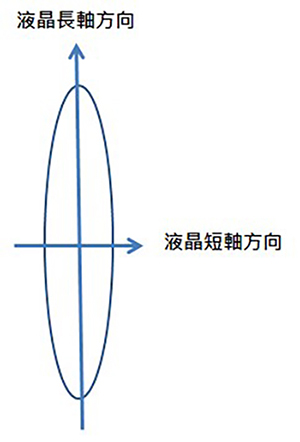
The long axes and short axes of liquid crystals, as shown in figure 3, lead to different levels of refraction. This phenomenon is called Birefringence.
LCDs adopt this unique optical trait of liquid crystals and show different brightness when the light travels through the liquid crystals at different angles.
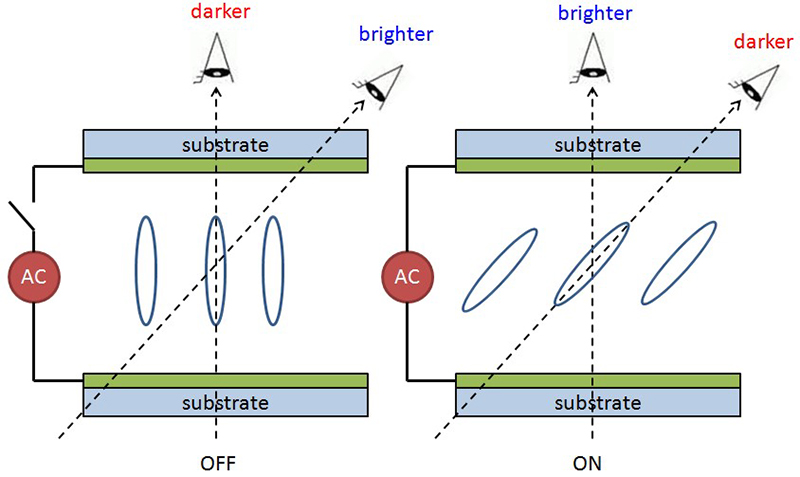
Brightness and contrast would look different from different viewing angles. It is because the observer would see more long axes of liquid crystals at one viewing angle and more short axes at other viewing angles. In the viewing angles where the short axes dominate, the observer can see the so-called grayscale inversion (the dark becomes brighter, and the white becomes darker), as shown in the figure. 4.
To address the issue of grayscale inversion, Winstar offers the solution to satisfy the wide-viewing angle requirement. As figure 5 shows, there is no grayscale inversion; therefore, it is highly applicable for the requirement where high contrast and wide viewing angle are needed.
■The mechanism of VATN full-view technology:
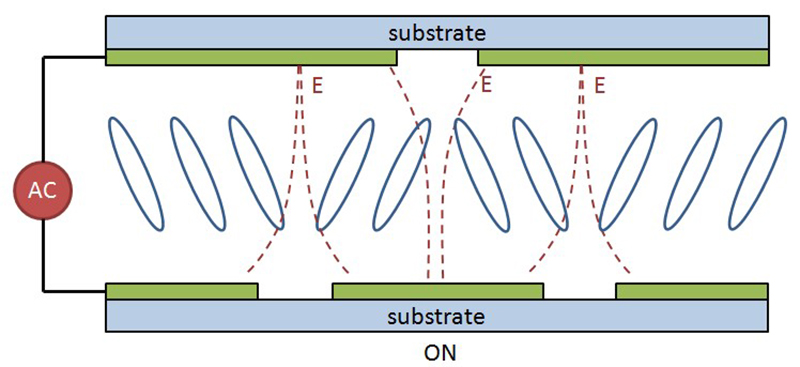
In order to improve the viewing angle blind area, the fringe electric field effect (Fringe-Field) is used to make the electrodes into a split gap structure with dislocations on the upper and lower sides to generate a symmetrical and curved electric field, so that the liquid crystal molecules are inclined in different directions after being affected by the electric field.
When it is not power-on, it is vertically aligned with general VATN liquid crystal molecules; but after power-on, the liquid crystal molecules have multiple inclination angles at the same time. People can see the multiple axes of the liquid crystal molecules at the same time from all view angles, and the deviation of brightness and darkness. Also, the degree of visual balance can be achieved, the contrast of various angles can be improved, and the viewing angle becomes wider, thus solving the original problem of grayscale inversion, as shown in Figure 6.
Winstar’s VATN full-view product features:
- High contrast ratio: up to 120:1
- Wide viewing angle: The widest viewing angle can reach to 170(H) 110(V).
- Mode: limited negative display mode (dark black background)
- Word color: white, can be matched with silk screen print, with customized color
- Duty requirements: ≤ 1/4Duty
- acklight colors: white/yellow-green/green/red/blue
Table 1: The difference between VATN wide viewing angle and general viewing angle
| Interface | Mask | View | Voltage | Duty | |
| General VATN | Zebra Heat Seal PIN | Film Mask | 3H/6H/9H/12H Blind zone in opposite way |
VOP>4.0V | Duty≤1/18 |
| COG | Cr Mask ×1 | ||||
| Wide viewing VATN | Zebra Heat Seal PIN COG | Cr Mask ×2 | Full view No blind zone | VOP>4.5V | Duty ≤ 1/4 |
PS. The wide viewing angle can solve the blind zone of the viewing angle, but the mold needs two pieces of Cr Mask, and the cost is slightly higher. In addition, most of the Duty recommends less than 1/4, and the VOP is slightly higher than the general VATN.


