Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a technology that allows a single Ethernet cable to transmit both data and power simultaneously. With PoE, devices like Wireless Access Points (WAP), IP cameras, and VoIP phones no longer require separate power lines, simplifying cabling requirements. As the IoT era has arrived, PoE applications have expanded from early IP phones to various products such as IP speakers, IP displays, Panel PCs, smart lighting, IoT sensors, and more. PoE is now widely used in smart homes, smart healthcare, industrial automation, and smart cities.
How PoE Simplifies Modern Device Deployment
PoE technology, by transmitting power and data through a single cable, offers several advantages for modern device deployment:
- Wireless Access Points (WAPs): Eliminates the need for separate power sources, simplifying wireless network installation.
- IP Cameras: Enables more flexible installation of surveillance systems, especially in areas where power outlets are difficult to install.
- VoIP Phones: Transmit both power and data through a single cable, reducing cable clutter and lowering installation costs.
- LED Smart Lighting: Provides power and network control through Ethernet, enabling efficient smart lighting systems.
Advantages of PoE
- Cost Savings: PoE eliminates the need for separate power lines, especially in retrofit projects, reducing installation and maintenance costs.
- Flexibility: Devices can be installed in locations without power outlets, providing greater freedom in deployment.
- Safety: PoE provides low-voltage power and includes built-in short-circuit protection mechanisms, ensuring equipment safety.
- Scalability: PoE easily integrates with existing networks, supports remote management, and enhances system flexibility and efficiency.
PoE Market Trends
As demand for IoT devices and smart buildings grows, the global PoE market is rapidly expanding. Reports show that the demand for PoE devices across various industries continues to rise, with significant growth potential expected in the future.
PoE Standards and Specifications
PoE technology is governed by several IEEE standards. The major ones are:
- IEEE 802.3af (PoE): Provides up to 15.4W of power per device, with approximately 12.95W available for use.
- IEEE 802.3at (PoE+): Provides up to 25.5W of power.
- IEEE 802.3bt (PoE++): Provides up to 60W or 100W of power, suitable for high-power devices.
PoE Standards
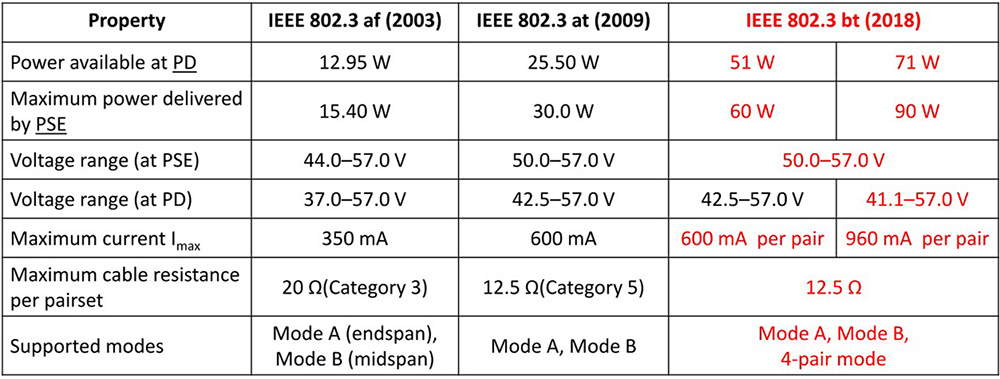
PoE Classification
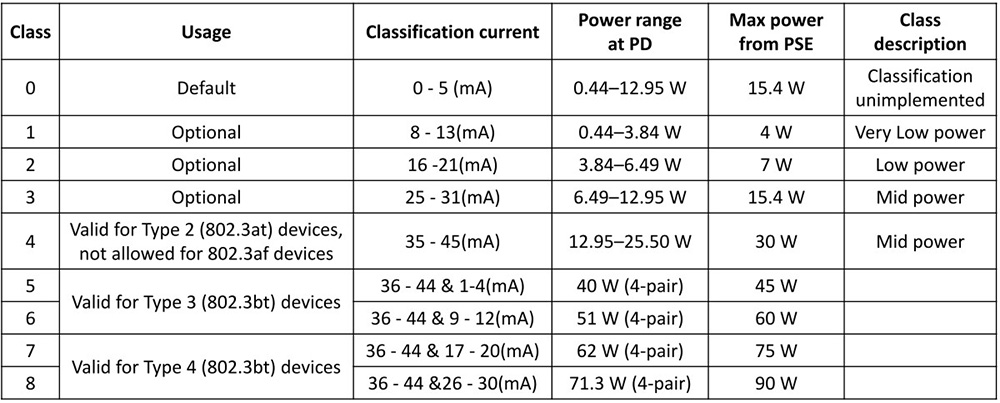
Excerpt from MITS Component & System Corp
PoE Detection Mechanism
Before providing power, PoE systems go through a three-step detection process:
- Detection: The power sourcing equipment (PSE) checks if the powered device (PD) is PoE-compatible, preventing power from being supplied to non-PoE devices.
- Classification: The system adjusts the power supply based on the device’s power requirements.
- Maintain Power Signature: Power supply is continuously monitored, and the system will stop supplying power if any abnormalities are detected to protect the equipment.
PoE Architecture
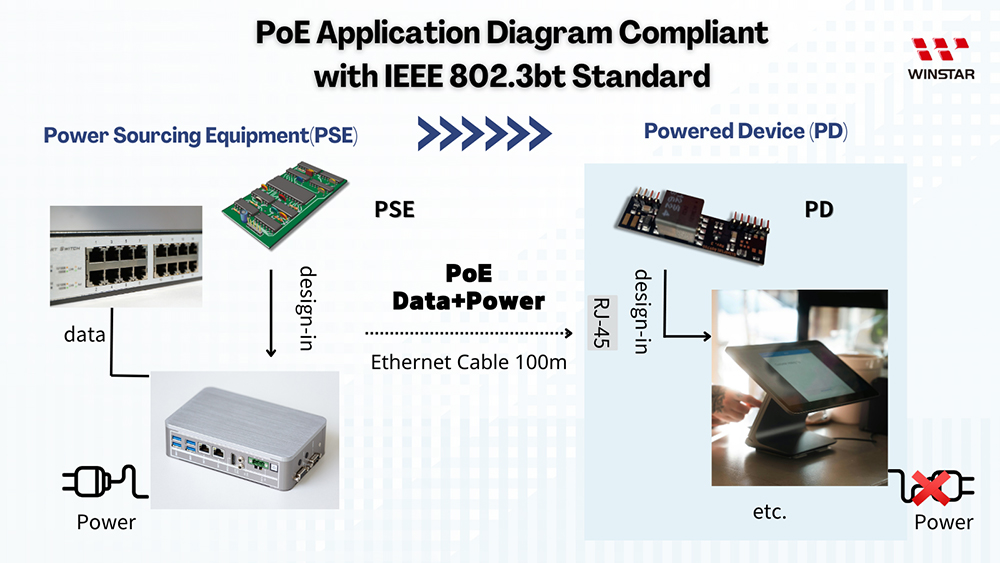
PoE Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) and Powered Device (PD)
Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE):
Ethernet cables don't naturally carry power, so the primary function of PSE is to inject power into the cable. PSE devices that comply with IEEE standards also have PoE detection capabilities to ensure network equipment operates safely. PSE devices are divided into two types:
- Mid-span Devices: Examples include PoE injectors and PoE adapters, typically single-port devices.
- End-span Devices: Examples include PoE switches, which are usually multi-port devices that integrate both Ethernet switching and PoE power supply functions.
Powered Device (PD):
Standard RJ45 interface devices cannot directly receive power through Ethernet cables. If non-IEEE compliant devices are used, they may lack detection mechanisms, potentially damaging equipment. PD devices connect to PoE in two main ways:
- Built-in PoE Functionality: Devices such as IP cameras, POS machines, Panel PCs, and IP speakers can integrate PoE modules to transmit power and data through Ethernet. If the device has built-in PoE PD functionality, it can receive power directly through the RJ45 interface. However, it’s important to ensure that the PSE provides sufficient power.
- External PoE Splitter: If the device does not have built-in PoE functionality, an external PoE splitter can be used. This separates the power and data from the Ethernet cable, providing DC power to the device while the Ethernet cable continues to transmit data.
Conclusion
PoE technology simplifies device deployment by transmitting both power and data through a single cable. As smart technologies continue to advance, PoE will play an increasingly vital role in future network and IoT applications.







